Amazon Web Services Tutorial
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a safe cloud services platform that offers database storage, compute power, content delivery and several other functionality that help the businesses grow. Just check online how millions of customers are presently leveraging AWS cloud products and solutions that build sophisticated applications with enlarged scalability, reliability and flexibility. In this tutorial, we will be covering several essential topics that will illustrate how AWS works and how it will turn out to be beneficial for running your website on Amazon Web Services.
Audience
This informative tutorial is made for the beginners who wish to learn how Amazon Web Services work for providing flexible, trustworthy and cost-efficient cloud computing services.
Amazon Web Services – Cloud Computing
Amazon Web Services started providing IT services from 2006 to the market in the form of web services that is popularly known as cloud computing these days. Because of this cloud, you no longer require to plan for servers and other IT infrastructure that takes up maximum of time in advance. Instead such services has the capability of spinning up thousands of servers in no time and deliver satisfying results quickly. In this process, you only pay for what you use with no up-front expenses and long duration commitments that makes AWS cost-effective.
Cloud Computing- Meaning
Cloud computing is basically an online computing service where numerous groups of remote servers are networked to permit centralized data storage, and online approach to computer resources or services.
By making use of cloud computing, companies can utilize shared computing and storage resources instead of building, improving and operating infrastructure on their own.
Cloud computing is such a model that comes equipped with following features:
- Users can provide or liberate resources on-demand.
- Depending on the overall load, resources can be scaled up or down on own.
- Resources can be accessed over a network with real security.
- Cloud service suppliers can easily permit a pay-as-you-go model, where customers are demanded based on the type of resources and per utilization.
Distinct Variety of Clouds
There are mainly three types of clouds: Private, Public and Hybrid.
Public Cloud
When talking about the public cloud, the third-party service providers design services and products that are made accessible to their customers via Internet. Customer’s data and related security are kept safe with the service providers’ owned infrastructure.
Private Cloud
Though the private cloud is known for offering almost same features as that of public cloud, but there is the major difference between both. In private cloud, the services and data are handled by the companies or by the third party only for the customer’s organization. In such a cloud, the maximum control is over the infrastructure so the queries related to security are curtailed.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud is basically a mix of both public and private cloud. The choice of running on public or private cloud generally depends on varied parameters like sensitivity of applications and data, industry certifications and needed regulations, standards and many more.
Cloud Service Models
There are three types of service models in cloud- IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
IaaS
IaaS generally stands for Infrastructure as a Service. It offers users with the ability to provision processing, network connectivity and storage on demand. Making use of this service model, the customers can easily evolve their own applications on such resources.
PaaS
In this section, the service provider offers varied services like queues, databases, e-mails, workflow engines, etc. to their customers. Later, the customers can make use of these components for creating their own applications. The service provider is responsible for managing the data backup, services and availability of resources that assist the customers in focusing more on the functionality of their application.
SaaS
As the name suggests, Software as a Service enables the third-party providers to offer the end-user applications to their prospective customers with some administrative ability at the application level such as the capability of handling and managing their users. Also at some point, customization is possible like customers can make use of their corporate logos, colors, etc.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Trustworthy:
A cloud computing platform is known for offering trustworthy, managed and consistent service than an in-house IT infrastructure. It assures 24X7 and 365 days of service. If any of such server fails, then hosted services and applications can easily be transferred to any of the present servers.
Recovery & Backup:
It is comparatively simple to store the data in the cloud, backing it up and restoring the same then storing it on a physical device. The cloud service providers like m365 business basic also come with sufficient technology for recovering the data which makes it simpler to recover the data anytime.
Cost-effective:
It is a tedious and costly process to construct your own servers and tools as you require to pay for, order, and configure costly hardware long before you need. However, when using cloud computing, you only require to pay the amount for what and when you use the computing resources. Thus, cloud computing is considered to be highly cost-efficient.
Trustworthy:
A cloud computing platform is known for offering trustworthy, managed and consistent service than an in-house IT infrastructure. It assures 24X7 and 365 days of service. If any of such server fails, then hosted services and applications can easily be transferred to any of the present servers.
Recovery & Backup:
It is comparatively simple to store the data in the cloud, backing it up and restoring the same then storing it on a physical device. The cloud service providers also come with sufficient technology for recovering the data which makes it simpler to recover the data anytime.
Cost-effective:
It is a tedious and costly process to construct your own servers and tools as you require to pay for, order, and configure costly hardware long before you need. However, when using cloud computing, you only require to pay the amount for what and when you use the computing resources. Thus, cloud computing is considered to be highly cost-efficient.
Amazon Web Services – Key Architecture
This is the general design of AWS EC2, wherein EC2 positions for Elastic Compute Cloud. EC2 enables the users to utilize the virtual machines of varied configurations according to their need. It enables distinct configuration options, varied pricing options, mapping of separate server and many more. These all features will be discussed in detail in AWS Products section. Go through the diagrammatic representation of the architecture.
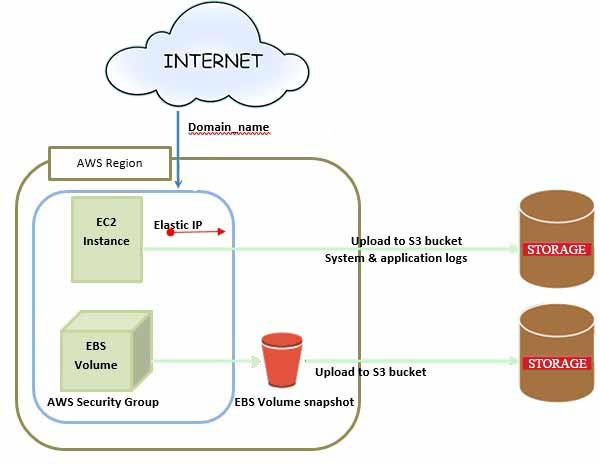 Note: In the given diagram, S3 is for Simple Storage Service. It enables the users to keep and recover distinct types of data making use of API calls. It doesn’t come with any computing element. These topics will be elaborated in detail in the AWS products section.
Note: In the given diagram, S3 is for Simple Storage Service. It enables the users to keep and recover distinct types of data making use of API calls. It doesn’t come with any computing element. These topics will be elaborated in detail in the AWS products section.
Load Balancing
In simpler terms, load balancing means to hardware or software load over web servers that boost the efficiency of the server along with the application. Above is the image that is representing the AWS architecture with load balancing.
Hardware load balancer is the most common network appliance that is being used in the traditional web application architectures.
AWS offers the Elastic Load Balancing service that distributes the traffic to EC2 instances across multifarious available sources and vital inclusion and removal of Amazon EC2 hosts from the load-balancing rotation.
Elastic Load Balancing can actively rise and shrink the load-balancing capacity for adjusting to traffic demands and also back sticky sessions in order to address the latest routing needs.
Amazon Cloud-front
Basically, Amazon Cloud-front is accountable for content delivery. It comes equipped with static, dynamic, and streaming content that makes use of a global network of edge locations. Requisition for content at the user’s end are routed to the closest location on own that revamps the performance.
Amazon Cloud-front is designed in a way that it works well with other Amazon Web Services such as Amazon EC2 and Amazon S3. Moreover, it also goes well with any non-AWS origin server and keeps the original files in the same manner.
No monthly commitments or contracts is there in the Amazon Web Services. You got to pay only for the part or little content that you deliver through the service.
Elastic Load Balancer
Elastic Load balancer is generally used for spreading the traffic to web servers that boost the overall performance. AWS offers the Elastic Load Balancing Service where the traffic is divided to EC2 instances over multifarious available zones and active addition and removal of EC2 hosts.
Security Management
Amazon’s Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) comes with a functionality called security groups that is identical to an inbound network firewall where you need to specify the ports, protocols, and source IP ranges that can reach to your EC2 instances.
Elastic Caches
Amazon Elastic Cache is basically a web service which handles the memory cache in the cloud. Cache plays a vital role in memory management as it helps in reducing the load on the services, boosts the overall performance and scalability on the database tier by caching recently used data.
Amazon RDS
Amazon RDS, a Relational Database Service is known for offering an identical access as that of Oracle, MySQL, or Microsoft SQL Server database engine. The same applications, queries and tools can be brought in use with Amazon RDS.
Hosting RDMS on EC2 Instances
Amazon RDS enables the users to integrate RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) of your wish such as Oracle, DB2, MySQL and many more on an EC2 instance and can handle as needed.
Amazon EC2 utilizes Amazon EBS just like network-attached storage. All the logs and data that run on EC2 instances must be placed on Amazon EBS volumes that will be available even if the database host fails. Making use of Amazon RDS, the service provider manages the storage and you only need to aim on handling the data.
Storage & Backups
There are several options available for accessing, storing and backing up web application data and assets. The Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) comes with a simple web-services interface that can be utilized for storing and recovering any amount of data at your desired time and place on the web.
Amazon S3 keeps the data as objects within the resources known as buckets. The users are provided with the option of keeping numerous objects as per their need within the bucket and can also write, read and delete the objects from the bucket.
The total capacity of Amazon EBS can be maximized up to 1 TB, and these volumes can be lined for big capacity and improved performance. Provisioned IOPS volumes are created in order to meet the needs of database workloads that are highly sensitive to storage performance and consistency.
Presently, Amazon EBS supports up to 1000 IOPS per volume. You can stripe multifarious volumes together seamlessly for delivering thousands of IOPS per instance to an application.
Auto Scaling
The major difference between AWS cloud architecture and the traditional hosting model is that AWS can actively scale the web application fleet on demand for managing the changes in traffic. But, when talking about the traditional hosting model, traffic forecasting model here are generally used to provide hosts ahead of projected traffic. In AWS, instances can be offered on the fly as per the set of triggers to scale the fleet out and back in.
AWS – Management Console
AWS Management Console is an ultimate web application that is known for managing Amazon Web Services. It comes with a range of services as well as provides the relevant information related to account like billing.
The console gives an inbuilt user interface for performing AWS tasks such as working with Amazon S3 buckets, connecting and launching to Amazon EC2 instances, setting Amazon CloudWatch alarms and many more.
This is the screenshot of AWS management console with respect to Amazon EC2 service.
Steps for accessing AWS
Step 1
Click on the services tab to know about the varied services.
 Step 2
Step 2
From the given list of categories, choose the apt option. After choosing, you will get their sub-categories as well.
Step 3
Choose the service of your wish and this will open the console of that service.
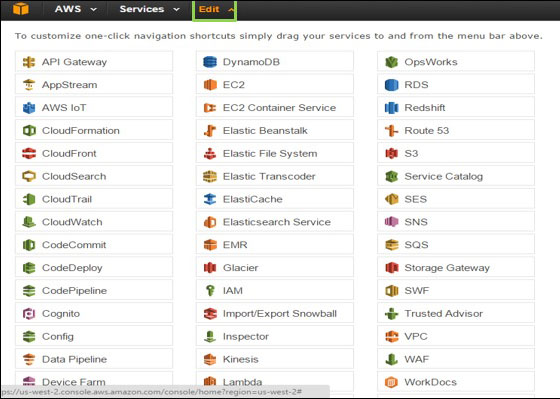
Customization Of Dashboard
Creation Of Services Shortcuts
On clicking the “Edit” menu on the navigation bar, a list of services appears. You can simply create their shortcuts by dragging them from the menu to the navigation bar.
Addition Of Services Shortcuts
On dragging the services from the menu to the navigation bar, the shortcut will be added and created and can also be arranged in any order. The screenshot given below shows the shortcut for S3, DynamoDB and EMR services.
Removal Of Services Shortcuts
In order to remove the shortcut, all you need to do is to click on the edit menu and drag the shortcut from the navigation bar to the service menu that will delete the shortcut.
Choosing The Region
As several services are region specific, thus it becomes vital to choose the region in order to manage the resources. There are some services that do not need a region to be selected like AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
In order to select a region, you first require to choose a service. For this purpose, click on the Oregon menu that appears on the left side of the console and after doing that choose a region.
Process Of Altering the Password
You can easily modify the password of your AWS account. Below given are the steps for this purpose:
Step 1
Click on the account name given on the left side of the navigation bar.
 Step 2
Step 2
On selecting the security credentials, a new page will appear with varied options. Choose the password options for changing the password and follow the given instructions.
Step 3
After signing-in, a page appears again with varied options for changing the password and following the instructions.
Once the process is successful, you will be getting a confirmation mail.
Know Your Billing Information
Go to the navigation bar and click on the account name. Then select the ‘Billing & Cost Management’ feature.
After this, a new page will appear with all the data related to money section. Making use of this service, you can easily pay AWS bills, monitor the usage and budget estimation.
Amazon Web Services – Console Mobile App
The console mobile app enables the users to go through the resources to select services. Moreover, it also supports a definite set of management functions for select resource types.
Below given are the varied services and supported functions that can be achieved using the mobile app.
EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud)
- Handle security group rules.
- Go through the blocked devices.
- Filter, browse and search instances.
S3
- Go through the properties of objects.
- Search buckets and see their properties.
Auto Scaling
- Depending on the situation, handle varied instances.
- Option of going through the group details, network settings and security.
Route 53
- Navigate and view hosted zones.
- Navigate and see details of record sets.
CloudWatch
- Examine CloudWatch graphs of resources.
- Action composition for alarms.
- Record CloudWatch alarms by time and status.
Process Of Using AWS Account
Below given are the steps to be followed for accessing AWS services-
- Make an AWS account.
- Sign-up for AWS services.
- Set a unique password to access your account credentials.
- Turn on your services in credit section.
Make an AWS Account
An entirely active free account is offered by Amazon for one year for the users to utilize and grasp the varied components of AWS. You get access to several AWS services such as S3, EC2, DynamoDB and many others for free of cost.
Step 1
For creating an AWS account, you need to open this URL https://aws.amazon.com and sign-up for new account and log in the necessary details.
In case, you have an account, then you can easily log in using the existing AWS password.
Step 2
Complete the contact details form after giving your email address. Amazon utilizes the given information for invoicing, billing and identifying the account. Once the account is created, sign-up for the needed service.
Step 3
Provide the payment details for signing up for the services. Amazon deducts the minimal amount transaction against the card on the file for checking whether it is valid or not.
Step 4
Next step is to verify the identity. Amazon calls back to the user for verifying the contact number.
Step 5
Select a support plan and subscribe to one of the plans like Developer, Business or Enterprise.
Step 6
Final step takes you to confirmation page. Go to the given link to sign in again that redirects to management console.
AWS Account ID
The account ID comes of 12-digit numbers like 123456789000 and is utilized for constructing Amazon Resource Names (ARN). This unique ID helps differentiate your resources from other resources in AWS accounts.
In order to know the AWS account number, you need to click on the Support tab present on the upper side of the navigation bar in AWS management console.
Conical String User ID
Conical string user ID is a blend of alphanumeric characters like 1234abchgf678. Used in Amazon S3 bucket policy, this ID’s help is apt for cross-account access which means to get access resources in varied AWS account.
Account Alias
Account alias is basically the URL for your sign-in page and consists of the account ID by default. This URL can be customized with the company name and ca be overwritten the former one.
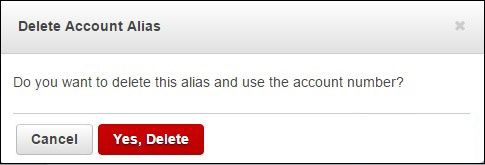
Procedure To Be Followed For Creating/Deleting Your Own AWS Account Alias?
Step 1
Sign in to the AWS management console and then use this link https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/ to open the IAM console.
Step 2
Choose the customization link and design an alias of choice.
Step 3
Click on the customize link to remove the alias and then click the Yes, Delete button. This process deletes the alias and reverts to the Account ID.
Multi Factor Authentication
Added on security is offered by Multi Factor Authentication by authenticating the users to put the unique authentication code from a certified authentication device or SMS text message at the time of accessing AWS websites or services. In case, the MFA code is correct, then only the users get the authority to access AWS services or else not.
Necessity
In order to utilize MFA services, the users need to assign a device (virtual or hardware) to IAM user or AWS root account. All the MFA device accredited to the users must be identical which means if the users wish to apply the code from another user’s device for authentication, then they can’t do so.
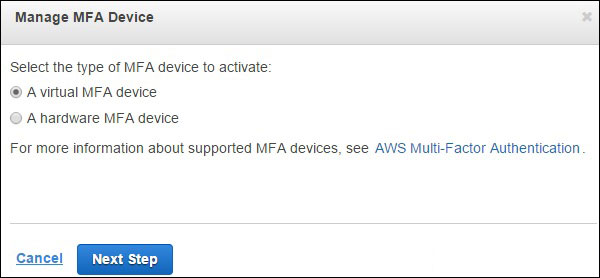
Process Of Enabling MFA Device?
Step 1
Open the URL, https:// console.aws.amazon.com/iam/
Step 2
Select users on the web page from the navigation pane on the right side for checking the list of user name.
Step 3
Select MFA by moving down to security credentials. Then click Activate MFA.
Step 4
By following the given instruction, you can easily activate the MFA device with the account.
These are the 3 methods for enabling the MFA device:
SMS MFA Device
In this process, MFA needs you to configure the IAM user with the valid phone number of the user’s SMS-compatible mobile device. Once the user logs in, AWS sends a six digit code by messaging to the user’s mobile. The user needs to use the same code as on the second web page during sign-in for authenticating the right user.
Hardware MFA Device
Here, MFA requires you to assign an MFA device (hardware) to the the AWS root account or the IAM user. A six-digit numeric code is generated by the device depending upon a time synchronized one-time password algorithm.
Virtual MFA Device
A virtual device is generally a software application that runs on a mobile device emulating a physical device. In this technique, MFA requires the people to assign an MFA device (virtual) to the IAM user or the AWS root account. A six-digit numeric code is generated based on a time-synchronized one-time password algorithm.
AWS Identity & Access Management (IAM)
IAM is basically a user entity that is created in AWS for representing a person who makes use of it with restricted access to resources. Thus, it is not vital to utilize the root account in everyday activities as the root account has limited access to the AWS resources.
Procedure Of Creating Users in IAM?
Step 1
Open the URL https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/ for logging in to AWS Management console.
Step 2
To open the complete file of all users, you need to choose the Users option available on the left navigation pane.
Step 3
You also get the option of creating New Users utilizing the Create new Users option, and this will open a new window. Choose the create option and a new user will be created.
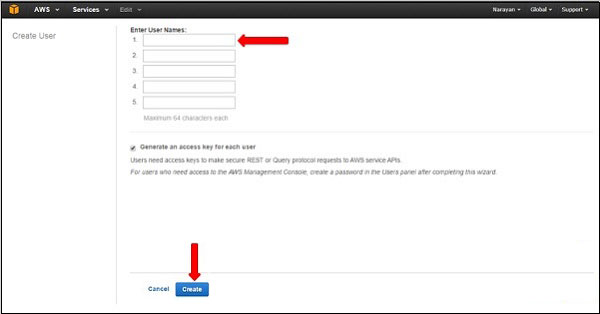
Step 4
You also get the access of Key IDs and secret keys by choosing Show Users Security Credentials link. Making use of the Download Credentials option, you can easily save the details on the computer.
Step 5
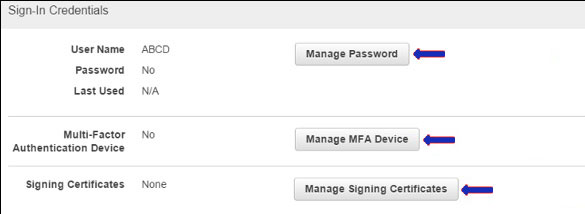
Finally, you can easily handle the user’s own security credentials such as managing MFA devices, creating password, creating/deleting the access keys and many more.
Wrapping Up!
To conclude, Amazon web services is extremely beneficial for the businesses. In today’s scenario, AWS has turned out to be a highly trustworthy, low-cost infrastructure platform in the cloud that powers several businesses in 190 countries all across the globe. This tutorial can be of great help for you to understand the cloud computing in detail.